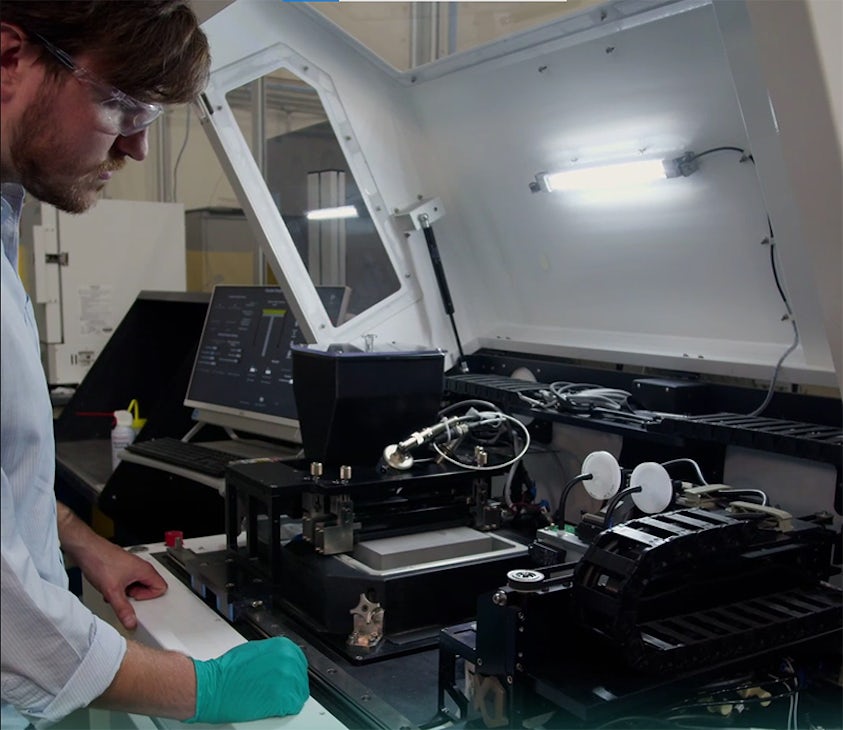
Material jetting is an additive manufacturing (AM) process in which droplets of liquid resin are selectively deposited via inkjet-style printheads and solidified by ultraviolet (UV) light exposure to build a solid 3D object.
Another AM process, vat photopolymerization, also works by selectively curing liquid photopolymer resins with light. However, whereas vat photopolymerization selectively cures resin in a holding tank, material jetting uses printheads to dispense resin while simultaneously curing it. Both material jetting and binder jetting use the same type of printhead technology – but while binder jetting deposits liquid adhesive onto another substrate, material jetting deposits the build materials that make up the final part and its support structures.
Material jetting is considered one of the most precise methods of additive manufacturing. Capable of printing in layers less than 20 microns thick, material jetting is known for building CAD designs with fine details, high accuracy, and smooth surfaces. Unfortunately, this level of fidelity can be time-intensive due to the number of layers. This can be offset somewhat by using multiple printheads simultaneously to build over a greater surface area. Extra printheads also allow for the use of multiple materials and colors in a single design.
These characteristics make material jetting ideally suited for realistic models, visual or haptic prototypes, tooling, and casting. However, due to the characteristics of cured photopolymers, the process is not usually recommended for printing functional or load-bearing components.
Related products: NX AM Fixed Plane | NX AM Multi-Axis | NX AM Build Optimizer