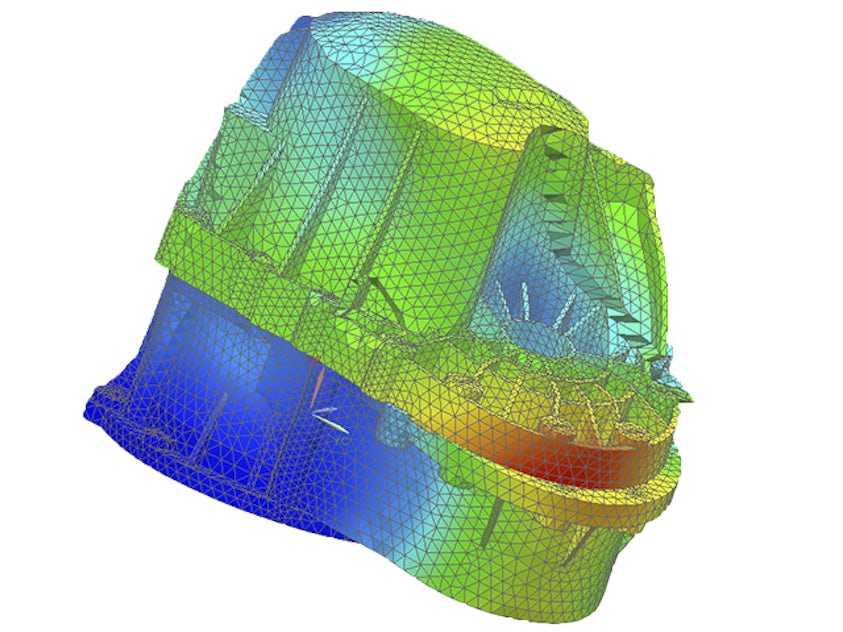
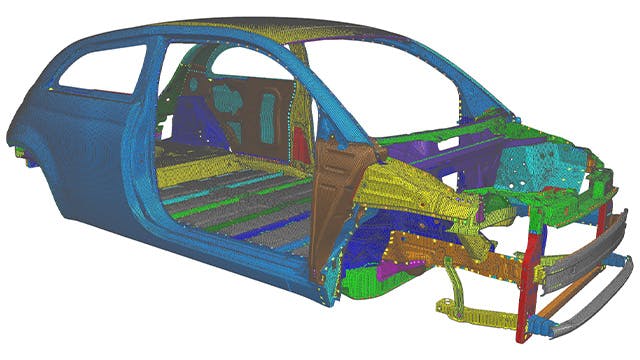
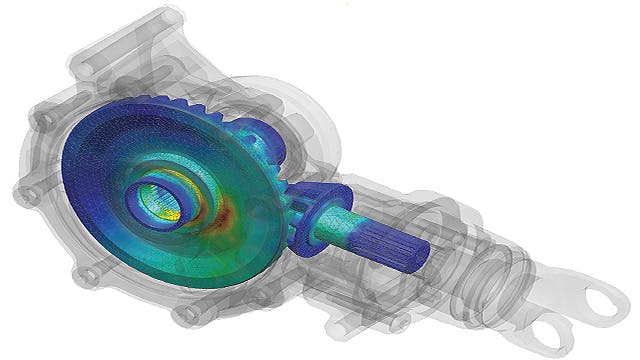
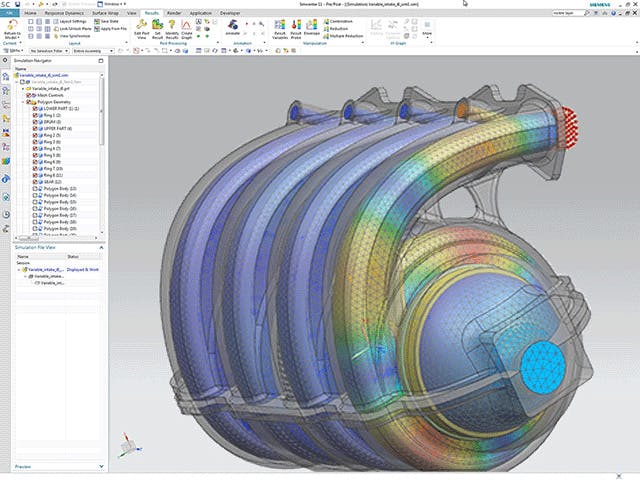
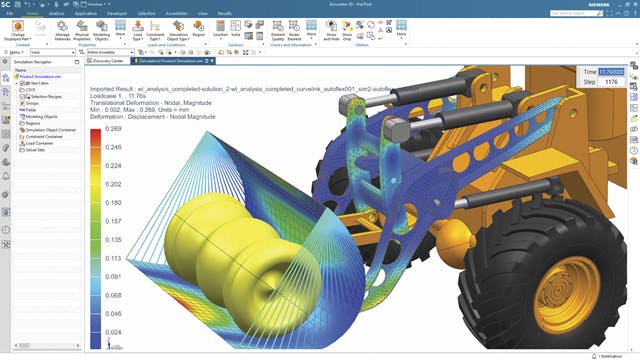
Finite element analysis is the modeling of products and systems in a virtual environment to find and solve potential (or existing) product performance issues. FEA is the practical application of the FEM, which is used by engineers and scientists to mathematically model and numerically solve complex structural, acoustic, electromagnetic, thermal, fluid and multiphysics problems. FEA software can be utilized in a wide range of industries but is most commonly used in the aeronautical, automotive, electronics, industrial machinery, marine and consumer product industries.
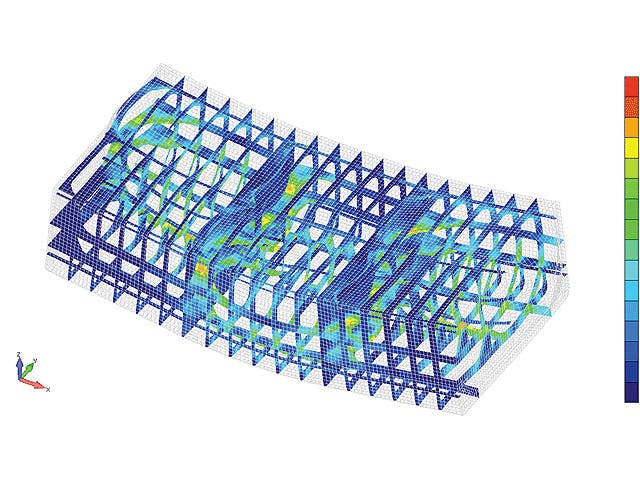
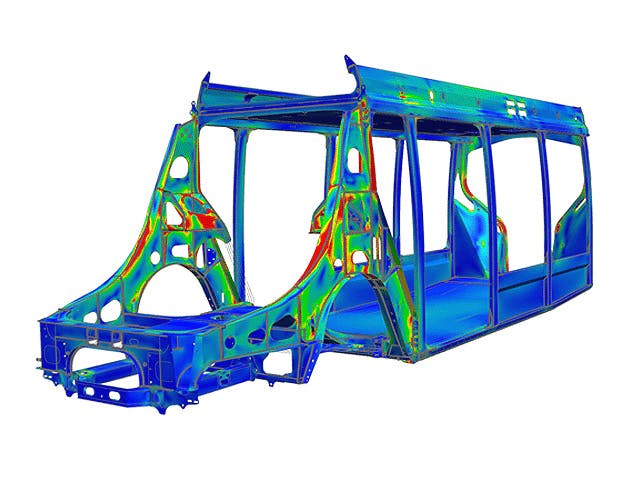
A finite element (FE) model comprises a system of points called "nodes," which form the shape of the design. Connected to these nodes are the finite elements that form the finite element mesh and contain the material and structural properties of the model, defining how it will react to certain conditions. The density of the finite element mesh may vary throughout the material, depending on the anticipated change in stress levels of a particular area. Regions that experience big changes in stress usually require a higher mesh density than those that experience little or no stress variation. Points of interest may include fracture points of previously tested material, fillets, corners, complex detail and high-stress areas.
Related products: Simcenter 3D | Simcenter Nastran | Simcenter Femap | Simcenter MAGNET | Simcenter E-machine design | Simcenter FLOEFD for NX