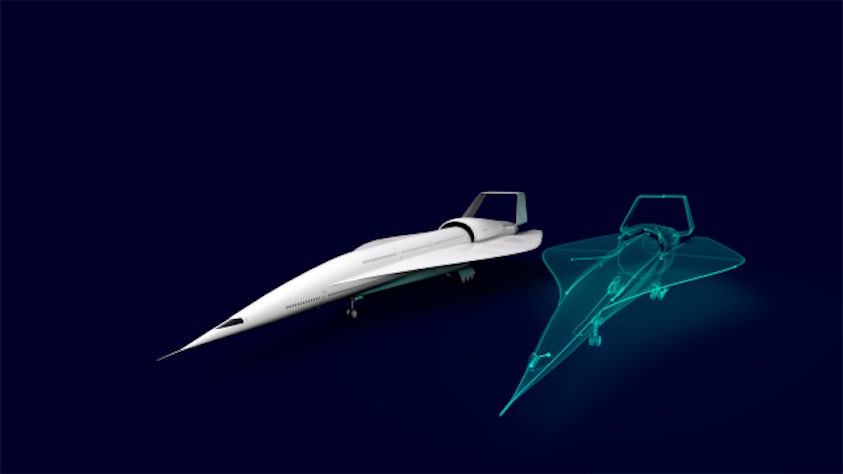
Unlike traditional digital twins, which are primarily used for monitoring and analysis, executable digital twins are active, dynamic models that can respond to inputs, simulate scenarios, and make decisions autonomously or with human intervention. The executable digital twin (or xDT). In simple terms, the xDT is the digital twin on a chip. The xDT uses data from a (relatively) small number of sensors embedded in the physical product to perform real-time simulations using reduced-order models. From those small numbers of sensors, it can predict the physical state at any point on the object (even in places where it would be impossible to place sensors).
Real-time simulation and interaction
Executable digital twins (xDT) are capable of simulating the behavior and performance of the physical asset or system in real time. They can respond to inputs, simulate different operating conditions, and interact with external systems or users dynamically.
Autonomy and decision-making
Executable digital twins (xDT) can make decisions autonomously based on predefined rules, algorithms or machine learning models. They can analyze data, predict outcomes and take actions to optimize performance or respond to changing conditions.
Closed-loop control
Executable digital twins (xDT) often operate in a closed-loop control system, where real-time data from sensors and actuators are fed back into the virtual model to adjust parameters, optimize performance and maintain desired operating conditions.
Predictive analysis and optimization
Executable digital twins(xDT) use predictive analytics and optimization techniques to forecast future behavior, identify potential issues or opportunities and recommend actions to improve performance or mitigate risks.
Integration with IoT and AI technologies
Executable digital twins(xDT) leverage Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, connectivity and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to collect real-time data, analyze complex patterns and make informed decisions. They may also incorporate machine learning models for adaptive behavior and continuous improvement.
Dynamic adaptation and learning
Executable digital twins(xDT) are capable of learning from experience and adapting to changes in the environment or operating conditions over time. They can continuously update their models, parameters and strategies based on new data and feedback.
Executable digital twins find applications across various industries, including manufacturing, energy, transportation, healthcare and smart cities. They enable predictive maintenance, autonomous operation, optimization of processes and decision support in complex systems where real-time monitoring and control are critical. Overall, executable digital twins represent the next evolution in digital twin technology, offering enhanced capabilities for real-time simulation, decision-making and optimization of physical assets and systems. An executable digital twin is an advanced form of a digital twin that not only represents a virtual replica of a physical asset or system but also has the capability to execute, simulate and interact with the virtual model in real time.
Physics-based models
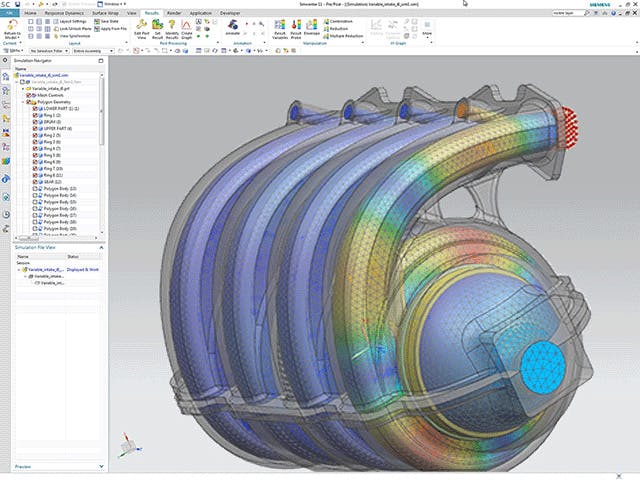
A physics-based executable digital twin relies on mathematical models that describe the physical behavior of the system being replicated. These models are typically based on fundamental principles of physics, such as mechanics, thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, electromagnetics, and so on. By solving the equations that govern these physical phenomena, the digital twin can simulate the behavior of the real-world system in a virtual environment.
Simulation of physical processes
The digital twin simulates the physical processes and interactions within the system using physics-based models. This allows it to predict how the system will behave under different operating conditions, inputs and scenarios.
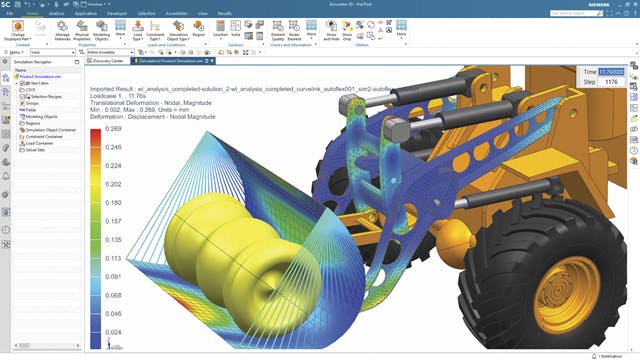
Real-time simulation
An executable digital twin based on physics models can simulate the behavior of the physical system in real-time or near-real-time. This enables dynamic interaction and decision-making based on the current state of the system and its environment.
Closed-loop control
Physics-based executable digital twins often operate in a closed-loop control system, where real-time data from sensors and actuators are used to adjust the simulation parameters and control the behavior of the virtual model. This allows the digital twin to maintain desired operating conditions and optimize performance.
Validation and verification
Physics-based models used in executable digital twins must be validated and verified to ensure their accuracy and reliability. This involves comparing simulation results with real-world measurements and experimental data to confirm that the digital twin accurately represents the physical system.
While physics-based modeling is commonly used in executable digital twins, it's important to note that other modeling approaches, such as data-driven modeling, empirical models, or hybrid models combining physics and data-driven techniques, may also be employed depending on the specific requirements and constraints of the application.