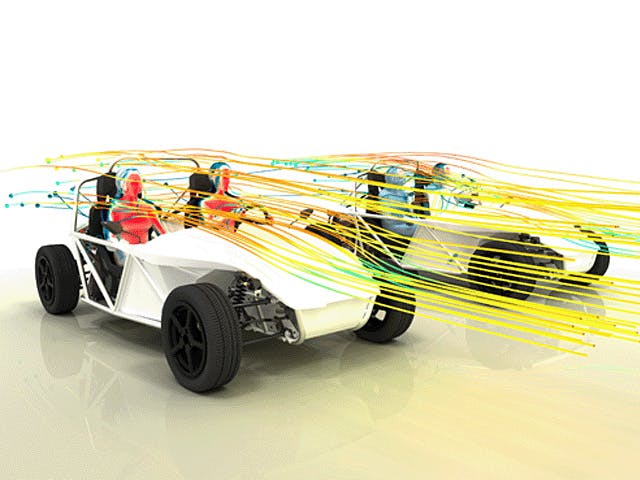
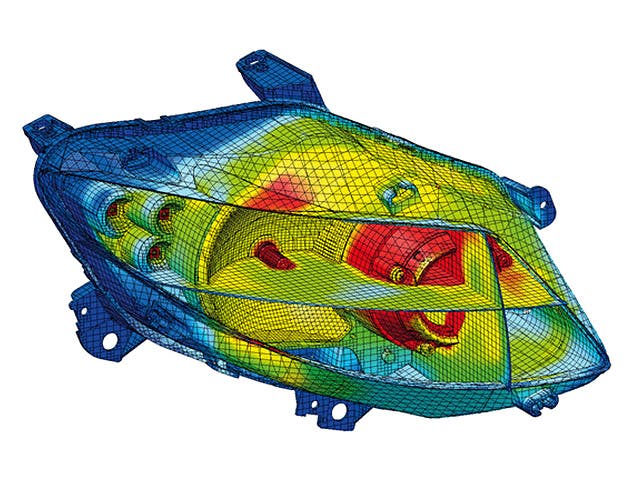
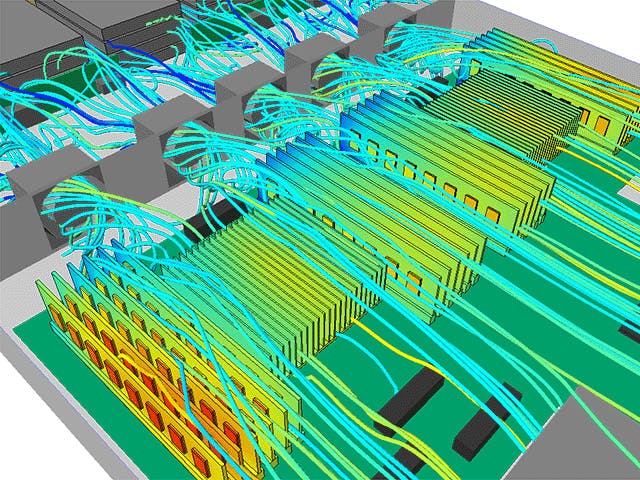
A computational fluid dynamics simulation involves using the fundamental laws of mechanics, governing equations of fluid dynamics and modeling to formulate a physical problem mathematically. Once formulated, computing resources use numerical methods to solve the equations using CFD software to obtain approximate solutions for the physical properties involved.
Computational fluid dynamics simulations are based on the Navier-Stokes equation, used to describe the motion of fluids. The accuracy of CFD simulations depends on the fidelity of the model, approximations and assumptions used, experimental validation and the computing resources available. It is essential to characterize the uncertainties and errors in the computational fluid dynamics simulation to use it as an effective tool in design and analysis.
There are three main methods of predicting the behavior of fluids and their interaction with the surrounding environment – experimental, analytical and numerical. Computational fluid dynamics is the numerical method of simulating steady and unsteady fluid motion using computational methods and hardware.
Computational fluid dynamics is a well-established methodology often used to replace or supplement experimental and analytical methods to aid the engineering design and analysis of everyday products.
Related products: Simcenter STAR-CCM+ | Simcenter FLOEFD | Simcenter Flotherm | Simcenter Flotherm XT | Simcenter Battery Design Studio