Binder jetting is a category of additive manufacturing (AM) techniques that use inkjet-style printheads to selectively deposit a liquid bonding agent onto powdered material to form solid, 3D objects. Because the powder molecules are bound together by an adhesive chemical reaction instead of melting or sintering from applied thermal energy, binder jetting techniques are distinct from powder bed fusion techniques.
Inkjet printing is commonly known as a type of 2D printing that recreates an image by propelling droplets of ink onto paper. The binder jetting process works similarly but uses liquid adhesive instead of ink and powdered substrate instead of paper. First, a thin layer of powder is spread flat over a build platform. Following the directions supplied by a CAD file, the printhead moves back and forth over the platform and selectively deposits droplets of bonding material to harden areas of powder. The build platform then changes height, another layer of powder is spread across the completed section, and the process is repeated layer by layer until the object is completely printed.
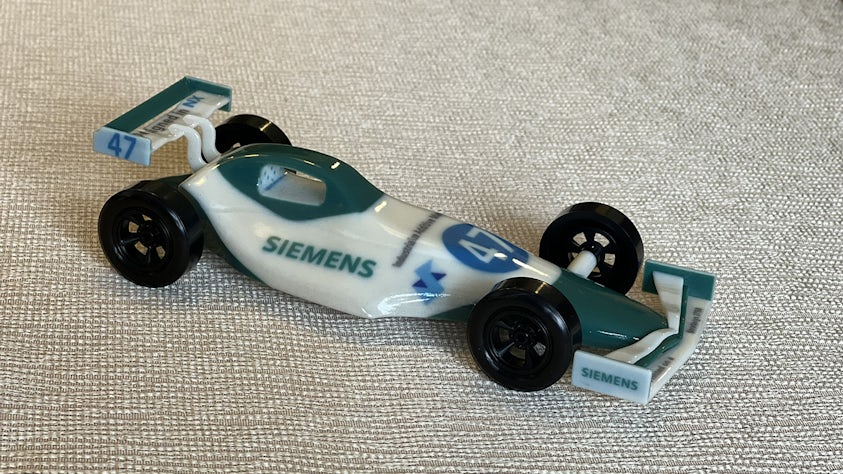
Binder jetting is a versatile additive manufacturing process that is compatible with a wide range of adhesives and powdered materials. By adding dyes to the adhesive and using additional printheads, binder jetting is one of the few additive manufacturing techniques that can print multicolored objects, making it ideal for aesthetic applications such as architectural mock-ups or decorative models. However, the resulting parts have little density and tend to be structurally weak – so binder jetting is typically not recommended for creating parts that need to bear loads or handle mechanical stress. On its own, binder jetting is a fast and inexpensive process. But, depending on the application, post-processing of the printed parts can add significant time and costs to the overall process.
Related products: NX AM Fixed Plane | NX AM Multi-Axis | NX AM Build Optimizer