Representing a physical object or body using a collection of points in space, 3D models connect by various geometric entities such as lines, triangles, curved surfaces, etc. A collection of data points, 3D models can be created manually, algorithmically or by using scanning software on their surfaces and may be further defined with texture mapping.
3D modeling describes the use of software tools, such as computer-aided design (CAD) programs, to create 3D digital representations of objects. Professions that use 3D modeling include consumer product development, automotive design, industrial equipment manufacturing, architecture, design, engineering, entertainment and gaming, as well as healthcare.
3D Modeling Software refers to software tools used to create three-dimensional models of objects or scenes. 3D modeling software can be used for various purposes beyond engineering and technical design, including animation, gaming, film, architecture and product design. These tools enable users to create, manipulate, and visualize 3D geometry using a variety of modeling techniques such as polygonal modeling, NURBS modeling, sculpting and procedural modeling.
The foundation of 3D models
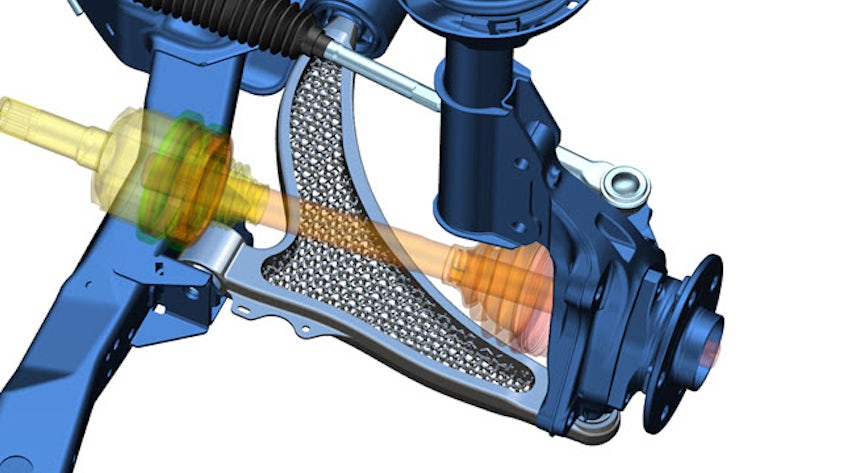
Although complex mathematical formulas are at the foundation of 3D modeling software, the programs automate computation for users and have tool-based user interfaces. 3D models are an output of 3D modeling and are based on a variety of digital representations. Boundary representation (B-rep) uses mathematically defined surfaces such as cones, spheres and NURBS (non-uniform rational basis spline) which are connected by topology to accurately represent objects as water-tight volumes. B-rep models are the preferred solution for engineering, and many 3D modeling applications for the design, simulation and manufacture of consumer and industrial products are B-rep based. Facet models approximate surfaces using connected planar polygons and are the preferred solution for less precise, high-speed, shape representations used in gaming, animation, and digital mock-ups.
Virtual 3D modeling
Virtual 3D models can be turned into physical objects through 3D printing or traditional manufacturing processes. Models can also be converted into static images through 3D rendering, commonly used to create photo-realistic representations for sales, marketing, and eCommerce applications. 3D models can be created by the process of reverse engineering, in which 3D scanning technology is used to create digital replicas of real-world objects, including manufactured parts and assemblies, free-form models designed in clay and human anatomy. Modern applications of 3D modeling create and interact with a “digital twin”, which is used to develop, test, simulate and manufacture its real-world counterpart as part of the product lifecycle.
Capabilities within 3D modeling
Visualize your product from any angle before manufacturing, or presentations to customers is by far the largest benefit of 3D modeling! With 3D modeling, you can virtually build and view every component of your product representing style, dimensions, color, and shapes bringing your product to life before manufacturing. 3D modeling aids in customizing and personalizing products for customers.
3D modeling software offers numerous benefits across various industries and applications.
Related products: NX CAD